技巧与窍门¶
This section covers various tips and tricks when using Rally in a recipe-style fashion.
对已存在的Elasticsearch集群做基准测试¶
警告
如果你刚开始使用 Rally,不了解其中的原理,请不要在任何生产环境或者类生产环境下运行它。另外,基准测试应该在专门的环境中执行,这样不会产生额外的流量偏差。
注解
我们假设在这个配置中,Rally 已经被正确 配置
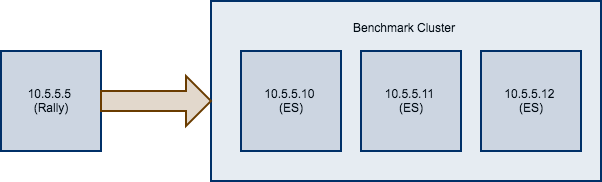
考虑以下配置:你有一个做基准测试的集群,由三个 Elasticsearch 节点组成: 10.5.5.10 , 10.5.5.11 , 10.5.5.12 。你已经设置了集群,并且你希望用 Rally 来做基准测试。Rally 安装在 10.5.5.5 。
首先,我们需要选择一个 track。运行 esrally list tracks:
Name Description Documents Compressed Size Uncompressed Size Default Challenge All Challenges
---------- ------------------------------------------------- ----------- ----------------- ------------------- ----------------------- ---------------------------
geonames POIs from Geonames 11396505 252.4 MB 3.3 GB append-no-conflicts append-no-conflicts,appe...
geopoint Point coordinates from PlanetOSM 60844404 481.9 MB 2.3 GB append-no-conflicts append-no-conflicts,appe...
http_logs HTTP server log data 247249096 1.2 GB 31.1 GB append-no-conflicts append-no-conflicts,appe...
nested StackOverflow Q&A stored as nested docs 11203029 663.1 MB 3.4 GB nested-search-challenge nested-search-challenge,...
noaa Global daily weather measurements from NOAA 33659481 947.3 MB 9.0 GB append-no-conflicts append-no-conflicts,appe...
nyc_taxis Taxi rides in New York in 2015 165346692 4.5 GB 74.3 GB append-no-conflicts append-no-conflicts,appe...
percolator Percolator benchmark based on AOL queries 2000000 102.7 kB 104.9 MB append-no-conflicts append-no-conflicts,appe...
pmc Full text benchmark with academic papers from PMC 574199 5.5 GB 21.7 GB append-no-conflicts append-no-conflicts,appe...
我们对全文检索基准测试比较感兴趣,所以我们选择运行 pmc 。如果你有自己的数据集来做基准测试,请参考 定义你自己的基准测试 ;你将收集比默认track更有用和代表性的指标数据。
接下来,我们需要知道哪些机器是目标,这很简单,我们可以从上面的图表看出来。
最后,我们需要检查使用哪个 pipeline 。对于这个例子, benchmark-only pipeline 是合适的。因为我们不希望 Rally 为我们提供集群。
现在我们可以运行 Rally 了:
esrally --track=pmc --target-hosts=10.5.5.10:9200,10.5.5.11:9200,10.5.5.12:9200 --pipeline=benchmark-only
如果你开启了 X-Pack Security ,你还需要指定一些其他的参数来使用 https 和传递证书:
esrally --track=pmc --target-hosts=10.5.5.10:9243,10.5.5.11:9243,10.5.5.12:9243 --pipeline=benchmark-only --client-options="use_ssl:true,verify_certs:true,basic_auth_user:'elastic',basic_auth_password:'changeme'"
对远程集群做基准测试¶
与前一个配置相反,你希望 Rally 提供所有的集群节点。
我们将用下面的配置作为例子:
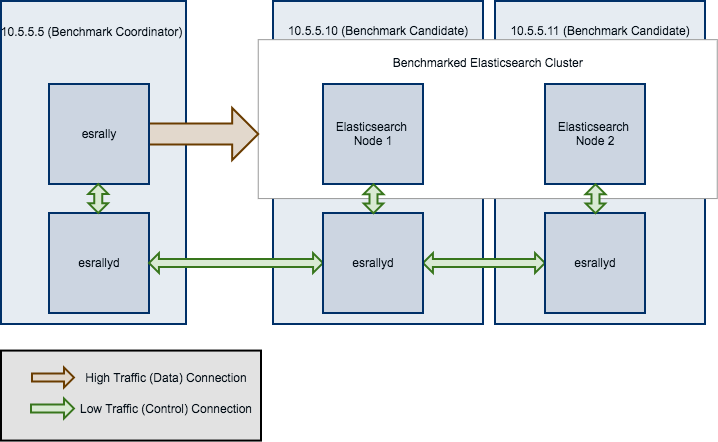
- 你将在
10.5.5.5启动 Rally。我们称这台机器为 “benchmark coordinator” 。 - 你的 Elasticsearch 集群包含两个节点:
10.5.5.10和10.5.5.11。我们称这些机器为 “benchmark candidate”s 。
注解
All esrallyd nodes form a cluster that communicates via the “benchmark coordinator”. For aesthetic reasons we do not show a direct connection between the “benchmark coordinator” and all nodes.
按照这些步骤来执行这个场景的基准测试:
- Install and configure Rally on all machines. Be sure that the same version is installed on all of them and fully configured.
- Start the Rally daemon on each machine. The Rally daemon allows Rally to communicate with all remote machines. On the benchmark coordinator run
esrallyd start --node-ip=10.5.5.5 --coordinator-ip=10.5.5.5and on the benchmark candidate machines runesrallyd start --node-ip=10.5.5.10 --coordinator-ip=10.5.5.5andesrallyd start --node-ip=10.5.5.11 --coordinator-ip=10.5.5.5respectively. The--node-ipparameter tells Rally the IP of the machine on which it is running. As some machines have more than one network interface, Rally will not attempt to auto-detect the machine IP. The--coordinator-ipparameter tells Rally the IP of the benchmark coordinator node. - Start the benchmark by invoking Rally as usual on the benchmark coordinator, for example:
esrally --distribution-version=5.0.0 --target-hosts=10.5.5.10:9200,10.5.5.11:9200. Rally will derive from the--target-hostsparameter that it should provision the nodes10.5.5.10and10.5.5.11. - After the benchmark has finished you can stop the Rally daemon again. On the benchmark coordinator and on the benchmark candidates run
esrallyd stop.
注解
Logs are managed per machine, so all relevant log files and also telemetry output is stored on the benchmark candidates but not on the benchmark coordinator.
Now you might ask yourself what the differences to benchmarks of existing clusters are. In general you should aim to give Rally as much control as possible as benchmark are easier reproducible and you get more metrics. The following table provides some guidance on when to choose which option:
| Your requirement | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| You want to use Rally’s telemetry devices | Use Rally daemon, as it can provision the remote node for you |
| You want to benchmark a source build of Elasticsearch | Use Rally daemon, as it can build Elasticsearch for you |
| You want to tweak the cluster configuration yourself | Use Rally daemon with a custom configuration or set up the cluster by yourself and use --pipeline=benchmark-only |
| You need to run a benchmark with plugins | Use Rally daemon if the plugins are supported or set up the cluster by yourself and use --pipeline=benchmark-only |
| You need to run a benchmark against multiple nodes | Use Rally daemon if all nodes can be configured identically. For more complex cases, set up the cluster by yourself and use --pipeline=benchmark-only |
Rally daemon will be able to cover most of the cases described above in the future so there should be almost no case where you need to use the benchmark-only pipeline.
Distributing the load test driver¶
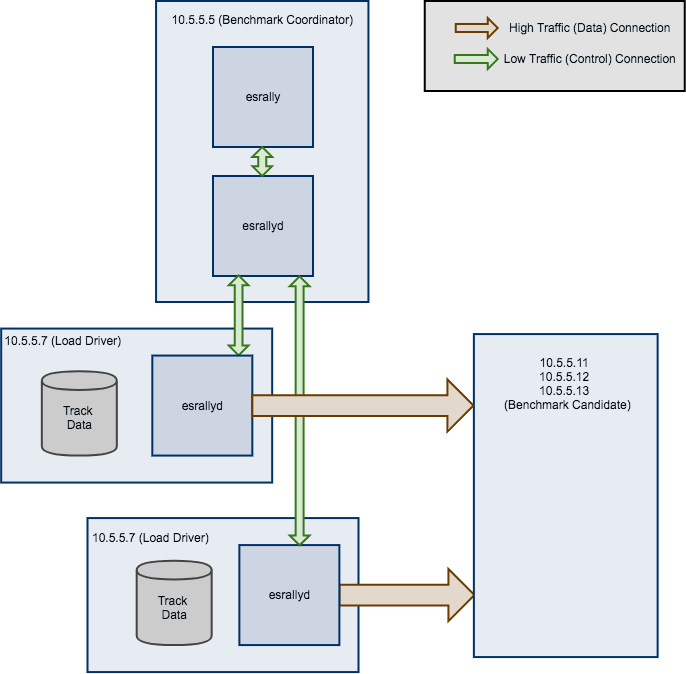
By default, Rally will generate load on the same machine where you start a benchmark. However, when you are benchmarking larger clusters, a single load test driver machine may not be able to generate sufficient load. In these cases, you should use multiple load driver machines. We will use the following configuration for the example:
- You will start Rally on
10.5.5.5. We will call this machine the “benchmark coordinator”. - You will start two load drivers on
10.5.5.6and10.5.5.7. Note that one load driver will simulate multiple clients. Rally will simply assign clients to load driver machines in a round-robin fashion. - Your Elasticsearch cluster will consist of three nodes which run on
10.5.5.11,10.5.5.12and10.5.5.13. We will call these machines the “benchmark candidate”. For simplicity, we will assume an externally provisioned cluster but you can also use Rally to setup the cluster for you (see above).
- Install and configure Rally on all machines. Be sure that the same version is installed on all of them and fully configured.
- Start the Rally daemon on each machine. The Rally daemon allows Rally to communicate with all remote machines. On the benchmark coordinator run
esrallyd start --node-ip=10.5.5.5 --coordinator-ip=10.5.5.5and on the load driver machines runesrallyd start --node-ip=10.5.5.6 --coordinator-ip=10.5.5.5andesrallyd start --node-ip=10.5.5.7 --coordinator-ip=10.5.5.5respectively. The--node-ipparameter tells Rally the IP of the machine on which it is running. As some machines have more than one network interface, Rally will not attempt to auto-detect the machine IP. The--coordinator-ipparameter tells Rally the IP of the benchmark coordinator node. - Start the benchmark by invoking Rally on the benchmark coordinator, for example:
esrally --pipeline=benchmark-only --load-driver-hosts=10.5.5.6,10.5.5.7 --target-hosts=10.5.5.11:9200,10.5.5.12:9200,10.5.5.13:9200. - After the benchmark has finished you can stop the Rally daemon again. On the benchmark coordinator and on the load driver machines run
esrallyd stop.
注解
Rally neither distributes code (i.e. custom runners or parameter sources) nor data automatically. You should place all tracks and their data on all machines in the same directory before starting the benchmark. Alternatively, you can store your track in a custom track repository.
注解
As indicated in the diagram, track data will be downloaded by each load driver machine separately. If you want to avoid that, you can run a benchmark once without distributing the load test driver (i.e. do not specify --load-driver-hosts) and then copy the contents of ~/.rally/benchmarks/data to all load driver machines.
修改默认的 track 仓库¶
Rally supports multiple track repositories. This allows you for example to have a separate company-internal repository for your own tracks that is separate from Rally’s default track repository. However, you always need to define --track-repository=my-custom-repository which can be cumbersome. If you want to avoid that and want Rally to use your own track repository by default you can just replace the default track repository definition in ~./rally/rally.ini. Consider this example:
...
[tracks]
default.url = git@github.com:elastic/rally-tracks.git
teamtrackrepo.url = git@example.org/myteam/my-tracks.git
If teamtrackrepo should be the default track repository, just define it as default.url. E.g.:
...
[tracks]
default.url = git@example.org/myteam/my-tracks.git
old-rally-default.url=git@github.com:elastic/rally-tracks.git
Also don’t forget to rename the folder of your local working copy as Rally will search for a track repository with the name default:
cd ~/.rally/benchmarks/tracks/
mv default old-rally-default
mv teamtrackrepo default
From now on, Rally will treat your repository as default and you need to run Rally with --track-repository=old-rally-default if you want to use the out-of-the-box Rally tracks.